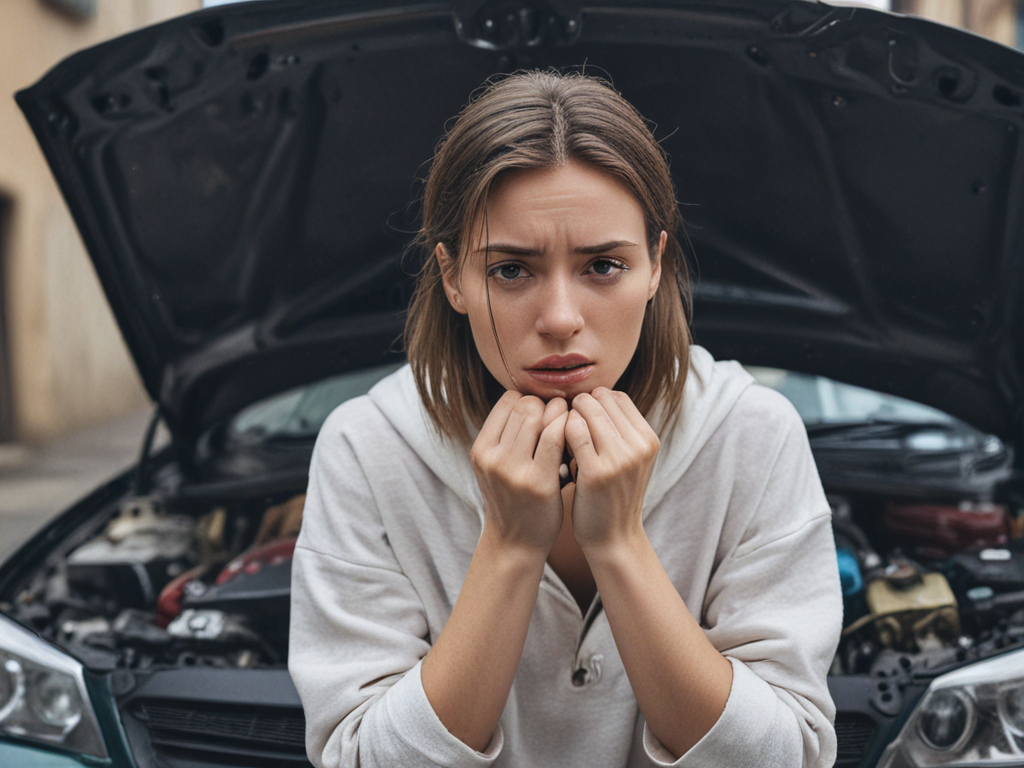
When your car refuses to start, it can feel like hitting a roadblock on a busy highway – frustrating and unexpected. The initial instinct might be to panic, but before you do, let’s calmly walk through a systematic approach to troubleshoot and potentially resolve the issue. From checking the battery to evaluating the security system, a methodical examination of key components can often disclose the underlying cause. So, let’s get started on unraveling this automotive mystery together.
Check the Battery
If your car won’t start, the first thing to check is the battery. Proper battery maintenance is essential for ensuring your vehicle starts reliably. One key aspect of battery maintenance is keeping the terminals clean and free of corrosion. This can be done using a mixture of water and baking soda applied with a small brush. Additionally, checking the battery’s fluid levels, if applicable, and ensuring they are topped up with distilled water is necessary for best performance.
When it comes to charging techniques, using a compatible charger is important. Avoid using incompatible chargers, as they can damage the battery. If you need to jump-start your car, connecting the jumper cables correctly is crucial. Remember, red clamps go to the positive terminals and black clamps to the negative terminals. Start the working car’s engine first, then try starting your car.
Regularly testing your battery’s charge level can help prevent unexpected starting issues. You can use a multimeter to check the voltage, aiming for around 12.6 volts for a fully charged battery. If your battery consistently fails to hold a charge, it may be time for a replacement. By following these battery maintenance tips and charging techniques, you can increase the chances of your car starting smoothly when you need it.
Inspect the Starter
After ensuring the battery is in good condition, the next step is to inspect the starter for any potential issues. When troubleshooting starter issues, it is important to follow a systematic approach to identify the root cause efficiently.
-
Listen for Starter Motor Noises: Start by turning the key in the ignition and listen for any unusual grinding or whining noises coming from the starter motor. Unusual sounds could indicate a problem with the starter.
-
Check Electrical Connections: Inspect the electrical connections to the starter motor for any signs of corrosion, loose wires, or frayed cables. Poor connections can prevent the starter from receiving the necessary power to start the engine.
-
Test the Starter Motor: Use a multimeter to check the voltage going to the starter motor. If the voltage is below the manufacturer’s specifications, it may indicate a faulty starter motor that needs to be replaced.
-
Inspect the Starter Solenoid: The starter solenoid plays an important role in engaging the starter motor. Check the solenoid for any visible damage or wear. A malfunctioning solenoid can prevent the starter from engaging properly.
Examine the Fuel System
When troubleshooting a car that won’t start, one important area to examine is the fuel system. Checking the fuel pump and inspecting the fuel injectors can help identify issues affecting the engine’s ability to receive the necessary fuel for ignition. Ensuring these components are functioning properly is essential in diagnosing and resolving starting problems related to fuel delivery.
Check Fuel Pump
Wondering how to determine if your fuel pump is causing your car not to start? Here are some fuel pump troubleshooting tips and common issues to check:
- Listen for a whirring noise near the gas tank when you turn the key; this indicates the fuel pump is operating.
- Check the fuel pump fuse and relay for any signs of damage or malfunction.
- Test the fuel pressure using a gauge to make sure the pump is delivering fuel at the correct pressure.
- Look for leaks in the fuel lines or a clogged fuel filter, which can strain the fuel pump and lead to starting issues.
These steps can help diagnose fuel pump-related problems efficiently.
Inspect Fuel Injectors
To further investigate potential causes of a car not starting, examining the fuel injectors within the fuel system is an essential step in diagnosing any underlying issues. Fuel injector cleaning can often resolve problems caused by clogs or buildup within the injectors, restoring proper fuel flow to the engine. If cleaning the injectors does not solve the issue, fuel injector replacement may be necessary. This involves swapping out the existing fuel injectors for new ones to secure peak performance. Regular maintenance, such as using fuel injector cleaners, can help prevent future issues and keep your car running smoothly. Below is a table highlighting the key differences between fuel injector cleaning and fuel injector replacement:
| Fuel Injector Cleaning | Fuel Injector Replacement |
|---|---|
| Clears clogs and buildup | Installs new injectors for peak performance |
| Maintains existing injectors | Secures proper fuel flow |
| Cost-effective solution | May be necessary if cleaning is unsuccessful |
| Preventative maintenance | Fixes more severe injector issues |
Assess the Ignition System
Evaluating the ignition system involves inspecting for spark, fuel delivery, and battery condition.
-
Check for Spark: Start by removing a spark plug wire and inserting a spare spark plug. Crank the engine and look for a spark. If there’s no spark, the ignition system may be faulty.
-
Inspect Fuel Delivery: Verify fuel is reaching the engine. Listen for the fuel pump to prime when you turn the key. Check fuel lines for any leaks or blockages that may prevent fuel from reaching the engine.
-
Assess Battery Condition: A weak or dead battery can result in a no-start situation. Test the battery using a multimeter to ensure it’s holding a charge. Clean any corrosion on the terminals that may impede proper connection.
-
Common Ignition System Issues: Look out for common problems like faulty spark plugs, a malfunctioning ignition coil, or a failing ignition switch. These components can often cause issues with starting the car and need to be checked and potentially replaced if found to be faulty.
Test the Alternator
Let’s move on to testing the alternator, an essential component in your car’s electrical system that guarantees the battery stays charged while the engine is running. The alternator plays a vital role in ensuring a healthy charging system for your vehicle. One common issue that can cause a car not to start is a malfunctioning alternator, which may result in a drained battery despite recent replacements.
To test the alternator, you can check the voltage output using a multimeter. Start by connecting the multimeter to the battery terminals while the engine is off; the voltage reading should typically be around 12.6 volts. Next, start the engine and observe the multimeter; the voltage should now read between 13.5 to 14.5 volts. If the voltage output falls outside of these ranges, it may indicate a problem with the alternator or the charging system.
A faulty alternator can lead to a drained battery, causing your car to fail to start. Monitoring the voltage output is a simple yet effective way to determine if the alternator is functioning correctly. If you suspect issues with the alternator, it is advisable to consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and address any problems with the charging system promptly.
Look at the Spark Plugs
When troubleshooting a car that won’t start, it’s essential to first look at the spark plugs. Check the spark plug connections for any loose or damaged wires, and inspect the condition of the spark plugs for signs of wear or fouling. Addressing any issues with the spark plugs can often resolve starting problems and get your car back on the road.
Check Spark Plug Connections
To properly check the spark plug connections, first, locate and inspect each spark plug for any signs of damage or wear. If everything looks fine, you can move on to checking the ignition and testing the coil pack. Here’s a simple guide to help you through the process:
- Confirm Ignition: Confirm that the ignition system is functioning correctly to provide the necessary spark to start the engine.
- Test Coil Pack: Test the coil pack for any faults or malfunction that may be hindering the spark plug performance.
- Inspect Spark Plug Wires: Make sure the spark plug wires are securely connected and in good condition.
- Clean Connections: Clean any dirt or debris around the spark plug connections to ensure a solid connection.
Inspect Spark Plug Condition
Inspecting the spark plug condition is important for diagnosing potential issues with your vehicle’s ignition system. Regular spark plug maintenance is essential for top engine performance. When checking the spark plugs, look for signs of wear, such as black carbon deposits or oil buildup. These can indicate problems like misfiring or inefficient combustion. If the spark plugs appear damaged or worn out, consider replacing them following manufacturer recommendations. Troubleshooting tips include ensuring the spark plugs are gapped correctly and are tightly secured in place. A faulty spark plug can lead to starting issues, poor fuel economy, and rough idling. By keeping an eye on your spark plug condition, you can address problems early and maintain your vehicle’s overall performance.
Check the Fuel Pump
If your car is having trouble starting, one critical component to check is the fuel pump. The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine, ensuring proper combustion and vehicle operation. Here’s how to troubleshoot and potentially replace a faulty fuel pump:
-
Listen for Fuel Pump Activation: When you turn the key in the ignition, listen for a faint whirring noise coming from the fuel tank area. If you don’t hear this sound, it could indicate a malfunctioning fuel pump.
-
Check Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to measure the pressure at the fuel rail. If the pressure is significantly lower than the manufacturer’s specifications, the fuel pump may be failing.
-
Inspect for Leaks: Look under the car for any signs of fuel leakage, which could be a result of a damaged fuel pump or its components.
-
Consider Fuel Pump Replacement: If troubleshooting indicates a faulty fuel pump and you have experience with automotive repairs, you may opt to replace the fuel pump. This process involves draining the fuel tank, safely removing the old pump, and installing a new one following manufacturer guidelines.
Evaluate the Engine
When evaluating the engine for starting issues, first check the spark plugs for signs of wear or damage. Worn-out or damaged spark plugs can prevent the engine from starting properly. If the spark plugs look good, the next step is to perform a compression test using a diagnostic tool. This test helps determine if there are any issues with the engine’s internal components affecting its ability to start.
If the engine is experiencing misfires, it could be due to various reasons such as faulty ignition coils, a clogged fuel injector, or even a vacuum leak. Troubleshooting steps involve checking these components systematically to identify the root cause of the misfire. Ignition coils should be inspected for cracks or damage, fuel injectors cleaned or replaced if necessary, and vacuum lines tested for leaks.
A compression test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can reveal issues like worn piston rings, damaged valves, or head gasket leaks. Low compression in one or more cylinders can cause starting problems and poor engine performance. By conducting a compression test, you can pinpoint internal engine issues that may be preventing your car from starting properly.
Scan for Error Codes
To further diagnose potential issues with your car’s starting problem, the next step is to scan for error codes using a diagnostic scanner. This tool, often referred to as an OBD scanner, connects to your vehicle’s onboard computer to retrieve error codes that can pinpoint the underlying problem.
Error Code Scanning Process:
-
Connect the OBD Scanner: Locate the OBD port in your car, typically found under the dashboard. Plug in the diagnostic scanner and turn on your vehicle to establish a connection.
-
Retrieve Error Codes: Initiate the scanning process on the diagnostic tool to read the error codes stored in the car’s computer system. These codes provide valuable insights into what may be causing the starting issue.
-
Error Code Troubleshooting: Once you have the error codes, research their meanings or consult a professional to interpret them. Each code corresponds to a specific problem area, aiding in targeted troubleshooting.
-
Implement Repair Solutions: Based on the identified error codes, proceed to address the root causes of the starting problem. This may involve replacing faulty components, repairing wiring issues, or clearing certain codes to resolve the issue efficiently.
Inspect the Fuses
Inspect the fuses in your car to check for any signs of damage or blown fuses that could be contributing to the starting issue. Common fuse issues can prevent your car from starting, so it is important to troubleshoot this component. Locate the fuse box, typically found under the dashboard or in the engine compartment. The fuse box cover usually has a diagram detailing which fuse corresponds to which component of the car.
To troubleshoot the fuses, visually inspect them for any signs of a broken filament inside the fuse. A blown fuse will show a gap in the metal strip or a darkened appearance. If you find a blown fuse, you can attempt a DIY fix by replacing it with a fuse of the same rating. Make sure to use the correct amperage to avoid damaging the vehicle’s electrical system.
Fuse replacement is a straightforward process, but if you are unsure or uncomfortable doing it yourself, seek assistance from a professional. Remember, fuses are vital for protecting the electrical components of your car, so it is important to address any issues promptly. By inspecting and replacing fuses as needed, you can eliminate a common starting problem and potentially get your car back on the road without the need for further diagnostics.
Check the Transmission
Let’s examine the transmission to determine if it may be the source of the starting issue. The transmission plays an important role in getting your car up and running. Here are some key points to think about:
-
Check Transmission Fluid: Low transmission fluid levels can cause issues with gear shifting and ultimately prevent the car from starting. Make sure the fluid is at the appropriate level as indicated in your vehicle’s manual.
-
Inspect for Leaks: Leaks in the transmission system can lead to a drop in fluid levels. Look under the car for any signs of leaking transmission fluid, such as red or brown puddles.
-
Test Gear Shifting: Try shifting gears to see if there are any unusual delays, grinding noises, or difficulty in getting into gear. Problems with gear shifting can indicate underlying transmission issues.
-
Transmission Warning Lights: If your car has a transmission warning light on the dashboard, pay attention to it. This light can signal potential problems with the transmission system that may be affecting the starting process.
Assess the Security System
How can we determine if the security system is causing the car starting issue? When faced with a car that won’t start, it is crucial to contemplate the security system as a potential culprit. Modern vehicles are equipped with advanced anti-theft systems that can sometimes malfunction and prevent the car from starting. Here are some key points to ponder when evaluating the security system:
| Issues | Symptoms | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Security System Bypass | Car fails to start even with a key fob | Consult the vehicle manual for steps on bypassing the security system. This can help start the car in case of a system malfunction. |
| Anti-Theft System Troubleshooting | Flashing dashboard light when trying to start the car | Check the battery of the key fob. If the battery is low, replace it. Make sure the key fob is within the range specified by the manufacturer for the system to function properly. |
Test the Electrical Connections
Testing the electrical connections is a critical step in diagnosing why your car won’t start. When the electrical system fails, it can prevent your car from starting altogether. Here are some essential tips to help you troubleshoot the electrical connections effectively:
-
Check the Battery: The battery is often the main culprit behind starting issues. Use a multimeter to test the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts. If it’s below 12 volts, the battery may need a recharge or replacement.
-
Inspect the Starter: A faulty starter can also lead to starting problems. Check the starter solenoid for any visible damage or wear. You can use a remote starter switch to bypass the ignition switch and test the starter directly.
-
Examine the Ignition Switch: The ignition switch plays a crucial role in sending power to the starter. If the switch is faulty, it may not transmit the necessary electrical signal. Test the ignition switch using a multimeter to make sure it’s functioning correctly.
-
Verify Ground Connections: Poor ground connections can disrupt the flow of electricity in your car. Inspect the ground cables for corrosion or looseness. Clean the connections and make sure they are tightly secured to restore proper electrical flow.
Consider Professional Help
If the electrical connections troubleshooting does not resolve the issue, seeking professional assistance can help diagnose and fix more complex car starting problems. When DIY troubleshooting fails to get your car started, it’s time to think about reaching out to a professional. Even if you’re knowledgeable about cars, some issues require specialized tools and expertise to identify and resolve.
Common issues that may require professional help include problems with the fuel system, ignition system, or internal engine components. These are areas where a professional mechanic’s experience can be invaluable in quickly pinpointing the root cause of the starting problem.
Professional help can also save you time and money in the long run. Attempting to fix complex issues without the right knowledge can lead to further damage to your vehicle. Mechanics have the training to efficiently diagnose the problem and make the necessary repairs, potentially saving you from more costly repairs down the road.
When your car won’t start, don’t hesitate to contact a trusted mechanic. They have the expertise to tackle even the trickiest car starting issues, getting you back on the road safely and swiftly.