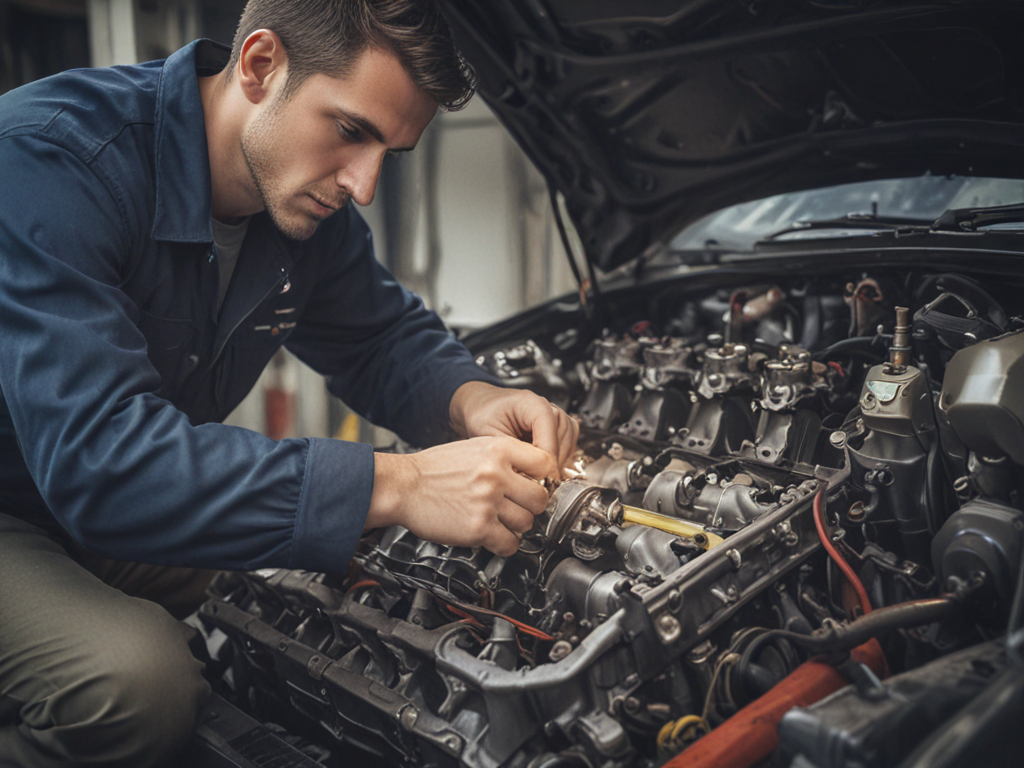
As an avid driver, you may not be aware that the coolant in your vehicle is not just a simple liquid – it plays a critical role in preventing overheating and engine damage. Maintaining the correct coolant levels and quality is paramount for the best functioning of your vehicle’s engine. Without proper coolant, the engine can quickly overheat, leading to costly repairs and potential breakdowns on the road. Understanding the basics of coolant composition, types, and functions can save you from these headaches while ensuring your engine runs smoothly.
Importance of Coolant
Coolant serves as the important liquid that absorbs and dissipates excess heat generated by the engine during operation. Proper coolant maintenance is essential for preventing overheating, which can lead to severe engine damage if left unchecked. Regularly checking the coolant level, quality, and ensuring it is at the correct concentration is key to the overall health and performance of the engine.
To maintain the coolant system effectively, it is necessary to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding coolant type and interval for replacement. Coolant should be changed at specified intervals to prevent it from losing its heat-dissipating properties over time. Additionally, checking for any leaks in the coolant system is crucial as even small leaks can lead to a loss of coolant, causing the engine to overheat.
Preventing overheating through proper coolant maintenance is not only about preserving the engine’s functionality but also about ensuring the safety of the vehicle and its occupants. Overheating can result in engine failure, leaving you stranded on the side of the road and potentially causing costly repairs. By staying proactive and attentive to coolant levels and quality, you can significantly reduce the risk of overheating and prolong the life of your engine. Remember, a well-maintained coolant system is key to a smoothly running engine and a trouble-free driving experience.
Coolant Composition
Having established the significance of maintaining coolant quality and levels to prevent engine overheating, understanding the composition of the coolant becomes imperative for ensuring peak performance and longevity of the cooling system. Coolant, commonly a mixture of water and ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, possesses properties essential for its function. These properties include high specific heat capacity, low viscosity, and anti-corrosive characteristics.
The primary role of coolant properties is to regulate the engine temperature by absorbing heat and transferring it to the radiator for dissipation. The high specific heat capacity of coolant allows it to absorb a considerable amount of heat before reaching its boiling point, ensuring efficient heat transfer. Additionally, the low viscosity of the coolant enables it to flow smoothly through the intricate network of cooling system components, facilitating heat exchange.
Corrosion prevention is another key aspect of coolant composition. Coolant contains additives such as corrosion inhibitors that protect the metal components of the engine from rust and corrosion. These inhibitors form a protective layer on the metal surfaces, preventing the formation of rust and extending the lifespan of the cooling system.
Understanding the composition of coolant and its properties is essential for maintaining an effective cooling system. By ensuring the coolant has the right properties and corrosion prevention measures, one can prevent overheating, corrosion-related damage, and ensure the longevity of the engine.
Coolant Types
I will now elaborate on the various types of coolants available for automotive use, their different compositions, and the importance of understanding the color-coding system associated with coolants. Additionally, I will explore the significance of using a coolant compatibility chart to guarantee the proper functioning and longevity of the cooling system in a vehicle. Understanding these key points will aid in maintaining the best engine temperature and preventing overheating issues.
Types of Coolant
Understanding the different formulations of coolant is important for maintaining the best engine temperature and performance. When comparing coolant types, one must consider the benefits each offers. Traditional green coolant, also known as ethylene glycol-based coolant, provides excellent corrosion protection and heat transfer properties. On the other hand, newer organic acid technology (OAT) coolants offer longer service intervals and reduced environmental impact. Hybrid organic acid technology (HOAT) coolants combine the advantages of both traditional and OAT coolants, providing extended service life and compatibility with various metals. Silicate-free coolants are ideal for aluminum engines due to their lack of silicates that can cause deposits. Selecting the right coolant type ensures optimal engine cooling and longevity.
Coolant Color Meaning
Exploring the various colors of coolant can provide valuable insights into the different types available and their specific properties. Coolant color is not just for aesthetics; it can indicate the type of additives and corrosion inhibitors present in the coolant. For example, green coolant typically contains silicate corrosion inhibitors, while orange coolant often includes organic acid technology. Understanding the significance of coolant color is important for proper coolant maintenance. By identifying the color of your coolant, you can make sure that you are using the correct type for your vehicle’s specific requirements. Regular coolant maintenance, including monitoring color changes and levels, is vital for preventing overheating and engine damage. Remember, the color of your coolant can speak volumes about its composition and effectiveness.
Coolant Compatibility Chart
Coolant types play a critical role in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s cooling system, and understanding their compatibility is essential for maintaining peak performance.
- Coolant Compatibility: It is important to use the correct type of coolant recommended by the vehicle manufacturer to prevent damage to the cooling system.
- Proper Dilution: Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for diluting coolant with water guarantees ideal heat transfer and protection against freezing and boiling.
- Avoid Mixing Coolants: Mixing different types of coolant can lead to chemical reactions, clogs, and reduced effectiveness in heat transfer.
- Regular Checks: Periodically inspecting the coolant level and quality can help identify any issues early on, preventing overheating and engine damage.
Coolant Function
The effectiveness of a vehicle’s cooling system relies heavily on the proper function of the coolant. As the engine operates, the coolant undergoes a crucial heat transfer process, absorbing heat from the engine and dissipating it through the radiator. Understanding the cooling system’s importance and the coolant’s role in managing engine temperature is fundamental to preventing overheating issues.
Cooling System Importance
Understanding the function of coolant within a vehicle’s cooling system is important for preventing overheating and ensuring peak engine performance. The cooling system plays a critical role in maintaining the engine’s temperature at best levels, safeguarding it from damage due to overheating. Here are four key reasons why the cooling system’s maintenance is essential for engine cooling efficiency:
- Regulates Temperature: Coolant absorbs heat from the engine and dissipates it through the radiator, preventing the engine from reaching dangerous temperatures.
- Prevents Corrosion: Proper coolant levels and quality help in preventing corrosion within the cooling system components, prolonging their lifespan.
- Ensures Efficient Heat Transfer: A well-maintained cooling system allows for efficient heat transfer, optimizing engine performance.
- Reduces Wear: By preventing overheating, the cooling system reduces wear on engine components, increasing their longevity and reliability.
Heat Transfer Process
To grasp the efficiency of engine cooling, it is imperative to comprehend the intricate process of heat transfer facilitated by the coolant within the vehicle’s system. Heat transfer mechanisms play a critical role in maintaining best engine temperature. As the coolant circulates through the engine, it absorbs heat generated during combustion. This heat is then transferred from the engine components to the coolant through conduction, convection, and radiation. The thermal conductivity properties of the coolant enable it to effectively carry heat away from the engine to the radiator, where it is dissipated into the surrounding air. Understanding these heat transfer mechanisms and the coolant’s thermal conductivity properties is fundamental to ensuring proper engine cooling and preventing overheating-related issues.
Signs of Low Coolant
Observing a decrease in coolant levels may indicate a potential issue with the cooling system. Detecting leaks or signs of low coolant is pivotal to prevent overheating and engine damage. Here are four key signs to look out for:
-
Visible Coolant Leaks: Check under the vehicle for any puddles or stains of bright-colored coolant, indicating a leak in the system. Leaks can occur at hose connections, the radiator, water pump, or the head gasket. Addressing leaks promptly prevents further coolant loss.
-
Engine Overheating: If your temperature gauge consistently shows higher-than-normal readings, it could be due to low coolant levels. Overheating symptoms like steam coming from the engine bay, a hot smell, or the temperature gauge in the red zone should not be ignored.
-
Low Coolant Warning Light: Some modern vehicles are equipped with a dashboard warning light that illuminates when coolant levels are low. If this light comes on, it is essential to top up the coolant to prevent overheating.
-
Reduced Cabin Heat: A decrease in the amount of warm air coming from your vehicle’s heating system can indicate low coolant levels. The coolant is responsible for transferring heat from the engine to the heater core, which then warms the air entering the cabin. If you notice a lack of heat, it may be due to insufficient coolant.
Checking Coolant Levels
Checking coolant levels is an essential part of maintaining a healthy cooling system and preventing potential overheating issues. To guarantee proper engine cooling, it is vital to monitor the coolant level regularly. Start by allowing the engine to cool down before opening the hood. Locate the coolant reservoir, which is typically a translucent plastic tank near the radiator. The coolant level should be between the minimum and maximum marks on the side of the reservoir. If the level is below the minimum mark, it indicates a potential leak or evaporation, requiring immediate attention.
Maintaining the correct coolant level is critical for the engine’s overall health. Low coolant levels can lead to overheating, causing significant damage to the engine components. Hence, it is advisable to top up the coolant with a mixture of equal parts coolant and distilled water to the recommended level. Regularly checking the coolant level can help prevent costly repairs and ensure excellent engine performance.
In addition to monitoring the coolant level, it is essential to inspect the coolant for signs of contamination or discoloration. Coolant should appear clear and brightly colored, indicating its effectiveness in cooling the engine. If the coolant appears dirty or rusty, it may be contaminated and require flushing. By following these maintenance tips and regularly checking the coolant level, you can help prevent overheating issues and prolong the life of your engine.
Coolant Flush Process
When conducting a coolant flush, the primary objective is to remove old coolant and contaminants from the cooling system. Coolant maintenance is vital for the best performance of the engine and the prevention of overheating. Here is a step-by-step guide to the flushing procedure:
-
Draining the Old Coolant: Begin by making sure the engine is cool. Place a drain pan beneath the radiator drain plug, typically located at the bottom of the radiator. Loosen the plug and let the old coolant drain completely.
-
Flushing with Water: After draining the old coolant, flush the system with water to remove any remaining debris or sludge. Close the drain plug, fill the system with water, start the engine, and let it run for a few minutes to circulate the water.
-
Adding Coolant Flush Solution: Once the system has been flushed with water, drain it again and add a coolant flush solution. This solution helps to break down any stubborn contaminants within the cooling system.
-
Refilling with New Coolant: Finally, drain out the flush solution, flush the system with water one last time, and refill it with a 50/50 mix of fresh coolant and distilled water to make sure proper coolant concentration.
Regular coolant maintenance, including a thorough flushing procedure, is essential to keep your engine running smoothly and prevent costly damage due to overheating.
Coolant Leak Detection
Upon inspecting a vehicle’s cooling system, a common indicator of potential issues is the presence of coolant leaks. Detecting coolant leaks promptly is important to prevent overheating and engine damage. There are various leak detection methods and maintenance practices that can help in identifying and addressing coolant leaks effectively.
Coolant Leak Detection Methods and Maintenance
| Leak Detection Methods | Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection for puddles under the vehicle | Regularly check coolant levels |
| Pressure testing the cooling system | Inspect hoses and connections for signs of wear |
| UV dye testing for hidden leaks | Look for white residue on components as a sign of leaks |
| Using a cooling system analyzer tool | Keep an eye out for steam or sweet-smelling odors |
Proper maintenance of the cooling system can also prevent coolant leaks. Regularly inspecting hoses, connections, and the radiator for any signs of wear can help detect leaks early. Addressing leaks promptly is essential to avoid costly repairs and potential engine damage. When repairing coolant leaks, it is important to use manufacturer-recommended coolant and follow proper procedures to ensure the cooling system functions optimally.
Coolant Replacement Frequency
I will now highlight the importance of coolant replacement frequency by examining ideal replacement intervals, signs that indicate coolant degradation, and the critical role fresh coolant plays in preventing overheating issues in a vehicle. By understanding these key points, we can effectively maintain the cooling system’s efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the engine. Regular coolant replacement is a fundamental aspect of vehicle maintenance that should not be overlooked for best performance and longevity.
Optimal Replacement Intervals
Optimizing the replacement intervals for coolant is important in maintaining the cooling system’s efficiency and preventing overheating issues. When considering the frequency of coolant replacement, it is essential to take into account the following factors:
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhering to the coolant replacement intervals recommended by the vehicle manufacturer guarantees best performance and longevity of the cooling system.
- Driving Conditions: Frequent short trips or stop-and-go driving may necessitate more frequent coolant changes to prevent overheating and maintain engine performance.
- Coolant Type: Different types of coolants have varying lifespans, so it is important to follow guidelines specific to the coolant being used.
- Coolant Condition: Regularly inspecting the coolant for signs of degradation can help determine if an earlier replacement is needed to safeguard the cooling system and engine performance.
Signs of Coolant Degradation
Inspecting coolant for signs of degradation is important to determining the appropriate replacement frequency to maintain the cooling system’s efficiency and prevent overheating issues. Coolant degradation indicators such as discoloration, presence of debris, and a strong acidic smell suggest the need for a coolant change. To guarantee ideal engine performance, it is vital to address these signs promptly through proper cooling system troubleshooting. Regularly monitoring the coolant’s condition can help identify potential problems early on, preventing costly repairs and engine damage. By staying proactive and attentive to coolant quality, you can extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s engine and avoid overheating complications.
| Coolant Degradation Indicators | Cooling System Troubleshooting | Replacement Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Discoloration | Debris Presence | Strong Acidic Smell |
| Rust Formation | Sediment Buildup | Change Every 2 Years |
| pH Level Change | Algae Growth | Or as Recommended |
Importance of Fresh Coolant
Maintaining a consistent coolant replacement schedule is important for best engine performance and to prevent potential overheating issues. Fresh coolant plays a vital role in the proper functioning of your vehicle’s cooling system. Here are four key reasons why timely coolant replacement is essential:
- Prevention of Corrosion: Fresh coolant helps prevent the formation of rust and corrosion within the cooling system.
- Best Heat Transfer: Regular coolant changes guarantee efficient heat transfer, keeping the engine at the right operating temperature.
- Protection Against Cavitation: Fresh coolant provides the necessary additives to prevent cavitation, which can lead to engine damage.
- Longevity of Cooling Components: Timely coolant replacement extends the lifespan of various cooling system components, reducing the risk of costly repairs.
Coolant and Engine Lifespan
Proper maintenance of coolant is essential for extending the lifespan of an engine. When coolant is functioning at its best, it plays a vital role in regulating the engine temperature, ensuring cooling efficiency, and promoting engine longevity. Coolant not only prevents overheating but also protects the engine from corrosion, rust, and scale buildup, which can greatly impact its lifespan.
To emphasize the importance of coolant maintenance, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Coolant Flush | Every 2 years | Removes contaminants and replenishes additives for optimal performance. |
| Check Coolant Levels | Monthly | Ensures proper coolant levels for consistent engine cooling. |
| Inspect for Leaks | Bi-annually | Detects potential issues early to prevent engine damage. |
| Use Distilled Water | When Topping Up | Prevents mineral buildup and maintains coolant effectiveness. |
| Monitor Coolant Color | Regularly | Different colors may indicate contamination or aging. |
Coolant Reservoir Maintenance
To confirm peak coolant functionality and overall engine health, diligent attention to the maintenance of the coolant reservoir is imperative. The coolant reservoir plays a critical role in the cooling system, acting as a storage tank for excess coolant and aiding in the prevention of overheating. Proper maintenance of the coolant reservoir is essential to guarantee its best performance and longevity.
-
Reservoir Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the coolant reservoir is necessary to prevent sediment buildup and contamination. Sediments and contaminants can hinder the effectiveness of the coolant and potentially lead to engine damage.
-
Coolant Contamination: Keep an eye out for any signs of coolant contamination in the reservoir. Contamination can occur due to mixing different types of coolant or external factors. Contaminated coolant should be drained and the system flushed to prevent any adverse effects.
-
Overflow Prevention: Check the reservoir for proper coolant levels regularly to avoid overflow. An overfilled reservoir can lead to leaks and unnecessary pressure on the cooling system.
-
Maintenance Tips: Inspect the reservoir for cracks, leaks, or any signs of damage. Additionally, make sure that the reservoir cap is tightly sealed to maintain the system’s pressure levels.
Coolant Mixing Guidelines
For best coolant performance and engine efficiency, understanding and following coolant mixing guidelines is essential. Proper mixing of coolant involves ensuring compatibility between different coolant types to prevent damage to the engine and maintain best performance. Below is a table outlining some key coolant compatibility guidelines to assist you in mixing the coolant correctly:
| Coolant Type | Compatible With |
|---|---|
| Ethylene Glycol | Most manufacturers recommend mixing with distilled water for best performance. |
| Propylene Glycol | Can be mixed with other propylene glycol-based coolants or diluted with distilled water. |
| Hybrid Organic Acid Technology (HOAT) | Should not be mixed with conventional coolants to maintain its effectiveness. |
It is important to always check the manufacturer’s guidelines on coolant compatibility before mixing different types of coolants. Improper mixing can lead to corrosion, buildup, and decreased coolant effectiveness. By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure that your engine is adequately protected and operating efficiently. Remember, the quality of the coolant mixture directly impacts the overall health and performance of your vehicle’s engine.
Coolant Overheating Causes
Understanding the root causes of coolant overheating in an engine is important for maintaining peak performance and preventing potential damage. As a service provider, identifying these causes can help in recommending preventive measures to ensure peak engine performance. Here are four common reasons for coolant overheating:
-
Low Coolant Levels: Insufficient coolant in the system can lead to overheating as there is not enough fluid to absorb and dissipate heat effectively. Regularly checking and topping up coolant levels is essential to prevent this issue.
-
Faulty Thermostat: A malfunctioning thermostat may get stuck in the closed position, preventing the flow of coolant through the engine. This obstruction can cause overheating by restricting the cooling process. Checking and replacing the thermostat as needed is important for maintaining proper engine temperature.
-
Coolant Leaks: Leaks in the cooling system can result in a loss of coolant, reducing the system’s ability to regulate temperature. Inspecting hoses, connections, and the radiator for leaks can help prevent coolant loss and subsequent overheating.
-
Cooling Fan Issues: A faulty cooling fan or fan relay can lead to inadequate airflow through the radiator, resulting in overheating. Regular inspection of the cooling fan, electrical connections, and relays can help ensure proper cooling system function and prevent engine overheating.
Coolant System Inspection
When conducting a coolant system inspection, it’s important to focus on visual inspection signs and fluid level checks. By visually evaluating for any leaks, corrosion, or damage to hoses, one can identify potential issues early on. Additionally, regularly monitoring the fluid level and condition guarantees ideal coolant performance and helps prevent overheating problems.
Visual Inspection Signs
Upon visual inspection of the coolant system, one can identify key signs that may indicate potential issues with overheating. It is important to conduct routine maintenance and visual inspections to prevent coolant leaks and detect problems early. Here are four visual inspection signs to watch for:
- Discolored Coolant: Look for coolant that appears rusty, indicating possible rust or corrosion within the system.
- White Smoke from Exhaust: White smoke could signal a coolant leak into the combustion chamber, leading to overheating.
- Visible Leaks: Check for puddles or drips under the vehicle, indicating a coolant leak that needs immediate attention.
- Bulging Hoses: Bulges in hoses suggest pressure build-up and potential weaknesses that may lead to leaks.
Fluid Level Check
Inspecting the coolant system’s fluid level is a critical step in maintaining peak engine performance and preventing overheating issues. Regular fluid checks are essential for coolant level maintenance, ensuring proper temperature regulation and preventing engine damage. Monitoring the coolant level helps to identify leaks, which can lead to overheating and potential engine failure if not addressed promptly. It is recommended to check the coolant level when the engine is cold to avoid burns and inaccuracies. If the level is low, it may indicate a leak or another underlying issue that needs attention. Proper coolant levels are crucial for the efficient operation of the engine cooling system.
| Importance of Coolant Level Maintenance | |
|---|---|
| Ensures Proper Temperature Regulation | |
| Prevents Engine Damage | |
| Identifies Leaks |