When it comes to diagnosing vehicle issues, mechanics often rely on tools that go beyond the surface. Just as a surgeon uses precision instruments, advanced diagnostic tools are the key to uncovering elusive problems in modern vehicles. From the intricate readings of OBD-II scanners to the detailed insights provided by oscilloscopes, these tools offer a deeper understanding of a car’s inner workings. But what about the lesser-known tools that could revolutionize your diagnostic process? Stay tuned to discover the advanced diagnostic tools every mechanic should have in their arsenal.
OBD-II Scanners
When diagnosing vehicle issues, mechanics often rely on OBD-II scanners for precise and efficient troubleshooting. These scanners are essential tools that connect to a vehicle’s onboard computer system to retrieve valuable information. One important aspect of using OBD-II scanners is sensor calibration. Ensuring that sensors are properly calibrated is essential for accurate readings and diagnosis. Without correct sensor calibration, the data provided by the OBD-II scanner may be skewed, leading to misinterpretation of the issue at hand.
Interpreting the data retrieved by OBD-II scanners is another critical skill for mechanics. Data interpretation involves analyzing the codes and information presented by the scanner to pinpoint the root cause of the problem. Understanding the significance of each code and its implications for the vehicle’s performance is key to effective troubleshooting. By mastering the art of data interpretation, mechanics can efficiently diagnose issues and provide timely solutions to their customers.
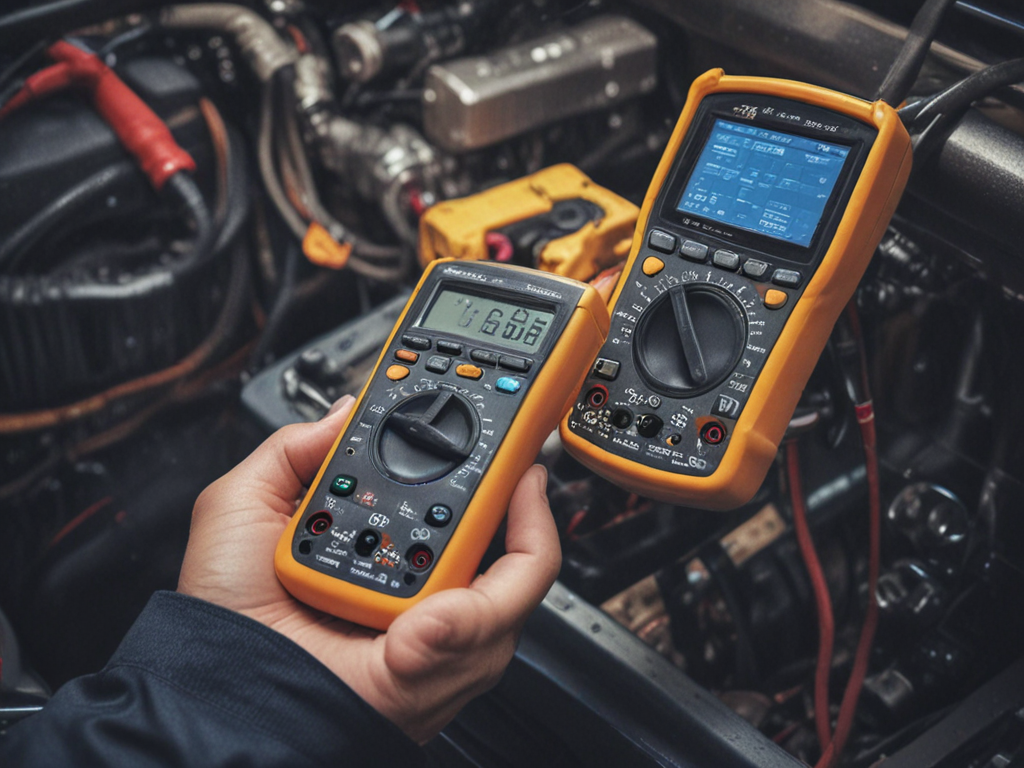
Multimeters
When it comes to advanced diagnostic tools for mechanics, multimeters are indispensable. One of the key aspects that mechanics can utilize multimeters for is voltage measurement techniques. Additionally, multimeters are vital for testing resistance in various automotive components.
Voltage Measurement Techniques
Utilizing a multimeter is essential for accurately measuring voltage in automotive diagnostics. When it comes to voltage measurement techniques, here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Voltage Drop Analysis – Use the multimeter to identify voltage drops across various components, pinpointing areas of concern.
- Waveform Interpretation – Analyze the electrical waveforms displayed on the multimeter to understand the quality of the voltage signal.
- Proper Settings – Ensure the multimeter is set to the correct voltage range to avoid inaccurate readings.
- Safety First – Always follow safety protocols when working with electrical systems to prevent accidents and damage.
Resistance Testing Methods
To effectively test resistance using multimeters, make sure the device is set to the appropriate setting for accurate readings. When conducting resistance measurement techniques, understanding Ohm’s law applications is essential for circuit analysis and electrical troubleshooting. By following these steps, you can efficiently diagnose circuit issues and guarantee accurate results. Below is a table summarizing common resistance testing methods using a multimeter:
| Testing Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Measurement | Measures the resistance of a component in a circuit | Diagnosing faulty components |
| Continuity Testing | Checks if a circuit is complete and has no breaks | Finding open circuits or broken wires |
| Resistance Range Setting | Adjusts the multimeter’s sensitivity for precise readings | Ensuring accurate measurements |
Understanding these methods and their applications can greatly enhance your diagnostic capabilities.
Oscilloscopes
Modern mechanics rely on oscilloscopes as essential diagnostic tools for pinpointing electrical issues in vehicles. Here are four key reasons why oscilloscopes are indispensable in the automotive industry:
-
Signal Analysis: Oscilloscopes allow me to analyze complex electrical signals with precision. By visually representing voltage changes over time, I can identify irregularities that may not be apparent through other testing methods.
-
Voltage Waveform Interpretation: Understanding voltage waveforms is vital for diagnosing issues like sensor malfunctions or faulty ignition systems. Oscilloscopes provide real-time data that helps me interpret these waveforms accurately.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy: With oscilloscopes, I can diagnose issues quickly and accurately, reducing the time spent on troubleshooting. This efficiency enables me to provide a faster turnaround time for customers, enhancing their overall satisfaction.
-
Versatility: Whether I’m working on engine sensors, ignition systems, or communication networks, oscilloscopes offer versatility across a wide range of automotive electrical systems. This adaptability makes them a valuable tool for tackling various diagnostic challenges in modern vehicles.
Fuel Pressure Testers
When it comes to diagnosing vehicle issues, fuel pressure testers are invaluable tools. They help determine if the fuel system is operating at the correct pressure levels, aiding in troubleshooting various engine problems efficiently. By using a pressure gauge, mechanics can pinpoint issues related to fuel delivery and make accurate assessments.
Pressure Gauge Usage
For accurate diagnosis of fuel system issues, mechanics rely on using pressure gauges, specifically fuel pressure testers. When dealing with pressure gauge usage, it is crucial to understand the following:
- Pressure Gauge Calibration: Proper calibration guarantees precise readings, leading to exact diagnostics.
- Troubleshooting with Precision: Advanced pressure gauge applications allow for detailed troubleshooting, pinpointing issues efficiently.
- Thorough Diagnostics: Utilizing fuel pressure testers enables detailed diagnostics, aiding in identifying complex fuel system problems.
- Efficient Problem-Solving: With the assistance of pressure gauges, mechanics can swiftly identify and address fuel system issues, minimizing downtime for the vehicle.
Troubleshooting Fuel System
Utilizing fuel pressure testers is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting fuel system issues accurately and efficiently. When dealing with fuel injector analysis or fuel pump diagnosis, these tools provide vital insights into the health of the system. Additionally, for tasks like throttle body troubleshooting and intake manifold examination, fuel pressure testers offer precise measurements that help pinpoint potential problems. Through a simple connection to the fuel rail, these testers provide real-time data on fuel pressure, enabling mechanics to identify issues swiftly. Below is a table illustrating the significance of fuel pressure testers in various fuel system diagnostics:
| Fuel System Diagnostic | Importance |
|---|---|
| Fuel Injector Analysis | Identifying injector issues |
| Fuel Pump Diagnosis | Evaluating fuel pump performance |
| Throttle Body Troubleshooting | Evaluating throttle response |
| Intake Manifold Examination | Detecting air/fuel mixture problems |
Compression Testers
Compression testers are essential tools used by mechanics to measure the pressure created during the compression stroke of an engine. This diagnostic tool provides important insights into the health and performance of an engine by evaluating the compression within its cylinders. Here are four key uses of compression testers:
-
Compression Ratio Analysis: By using a compression tester, mechanics can calculate the compression ratio of an engine. This ratio is essential in determining the engine’s efficiency and power output, providing valuable information for tuning and troubleshooting.
-
Cylinder Leakage Testing: Compression testers help identify any leakage within the cylinders of an engine. By conducting a cylinder leakage test, mechanics can pinpoint the source of compression loss, such as worn piston rings, damaged valves, or head gasket issues.
-
Detecting Engine Wear: A compression test can reveal signs of engine wear, such as low compression levels in specific cylinders. This information allows mechanics to address potential problems early, preventing further damage to the engine.
-
Verifying Engine Rebuilds: After performing an engine rebuild, mechanics can use a compression tester to verify that the cylinders are properly sealed and that the engine is functioning optimally.
Smoke Machines
When diagnosing engine issues, mechanics often turn to smoke machines as a powerful tool for pinpointing leaks and identifying potential problems. Smoke machines work by generating artificial smoke that is then pumped into the engine’s intake or EVAP system. The smoke will escape from any leaks, making them easy to detect. Here’s a breakdown of smoke machine applications, benefits, and troubleshooting tips:
| Smoke Machine Applications | Benefits | Troubleshooting Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Locating vacuum leaks in the intake system | – Quickly identifies leaks | – Check for loose connections and damaged hoses |
| Finding evaporative emissions leaks | – Helps meet emission standards | – Inspect the EVAP system components for cracks |
| Testing the integrity of the engine’s PCV system | – Prevents oil leaks | – Examine the PCV valve for proper function |
Using a smoke machine can save time and improve accuracy when diagnosing engine issues. However, to ensure effective results, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines. Additionally, regularly maintaining the smoke machine will guarantee its peak performance. With these applications, benefits, and troubleshooting techniques in mind, mastering the use of a smoke machine can become a valuable skill for any mechanic dedicated for precision in diagnostics.
Borescopes
Borescopes provide mechanics with a versatile and invaluable tool for inspecting hard-to-reach areas within an engine or machinery. These devices consist of a flexible tube with a camera at the end, allowing for visual inspection of areas that are otherwise inaccessible. Here are some key points to think about when using borescopes:
- Borescope Applications:
- Borescopes are commonly used for inspecting engine cylinders, valves, and pistons.
- They are also valuable for examining plumbing systems, HVAC ducts, and electrical installations.
- Borescopes play a critical role in aviation maintenance for inspecting turbine engines and aircraft components.
- In automotive repair, borescopes help diagnose issues within the transmission, exhaust system, and more.
- Borescope Limitations:
- Limited field of view: Borescopes can only visualize a small area at a time.
- Image quality: Lower-cost borescopes may have lower resolution cameras.
- Depth of field: Some borescopes struggle with focusing on objects at varying distances.
- Flexibility: The maneuverability of the probe may be restricted in complex systems.
When it comes to maintaining borescopes, regular upkeep is essential to make sure performance. Calibration of the device is important to maintain accuracy in inspections and guarantee reliable results. By understanding the applications and limitations of borescopes and conducting proper maintenance and calibration, mechanics can effectively utilize this advanced diagnostic tool in their work.
Infrared Thermometers
Utilizing infrared thermometers provides mechanics with a non-contact method for quickly and accurately measuring surface temperatures. These diagnostic tools are invaluable in the automotive industry for pinpointing temperature variations in engines, brakes, HVAC systems, and more. When it comes to temperature accuracy assessment, infrared thermometers offer a reliable solution, ensuring that mechanics can identify hotspots or abnormalities with precision.
In comparison to traditional contact thermometers, infrared thermometers excel in their efficiency and ease of use. By simply pointing the device at the target area, mechanics can instantly read the temperature without the need to physically touch the surface. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of burns or injuries when dealing with high-temperature components.
Additionally, infrared thermometers are versatile tools that can be used in various settings beyond automotive repair. From checking the temperature of tires to diagnosing cooling system issues, these devices prove to be indispensable for mechanics looking to work swiftly and accurately.
Battery Testers
As a mechanic, I rely on battery testers for two important functions: voltage testing and load testing. Voltage testing helps me determine if the battery has enough power to start the vehicle, while load testing assesses the battery’s ability to sustain power under a heavy load. These two tests are essential for diagnosing battery health and preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Voltage Testing
When testing vehicle batteries, a reliable battery tester is essential for accurately measuring voltage levels. Voltage drop analysis and circuit continuity testing are critical steps in diagnosing electrical issues. Here are key points to ponder:
- Choose the Right Tester: Select a battery tester that can measure both voltage and current accurately.
- Inspect Cables and Connections: Check for corrosion, loose connections, or damaged cables that may affect voltage readings.
- Follow Safety Protocols: Always wear appropriate safety gear when working with electrical systems.
- Interpret Results: Understand the readings to pinpoint potential problems accurately.
Using a quality battery tester and following these steps will help identify and resolve electrical issues effectively.
Load Testing
Load testing the battery with a reliable tester is essential for evaluating its performance under different conditions. Stress testing the battery through load testing helps in understanding how it performs when the demand is high, providing valuable insights for system optimization. By conducting load testing, mechanics can assess the battery’s ability to deliver power consistently, ensuring it meets the vehicle’s requirements. Additionally, load testing aids in load balancing, which is vital for the overall performance and longevity of the battery. Through performance analysis during load testing, mechanics can identify potential issues early on, allowing for proactive maintenance. Overall, incorporating load testing as part of diagnostic procedures enhances the accuracy of assessments and facilitates efficient problem-solving for best vehicle functioning.
Ignition Testers
Using an ignition tester is a vital step in diagnosing engine performance issues quickly and accurately. Ignition testers help pinpoint problems in the ignition system, which is essential for efficient troubleshooting. Here are some key aspects to take into account when using an ignition tester:
-
Spark Plug Analysis: An ignition tester can assess the condition of spark plugs by checking for proper firing. This analysis is important as faulty spark plugs can lead to engine misfires and poor performance.
-
Coil Diagnostics: Ignition testers can also evaluate the coils’ functionality by measuring the strength and consistency of the spark produced. Identifying weak or malfunctioning coils early on can prevent more significant issues down the line.
-
Ignition System Performance: By testing the ignition system, mechanics can make sure that all components are working together harmoniously to ignite the fuel-air mixture effectively. Any deviations from the best performance can be addressed promptly.
-
Misfire Detection: Ignition testers excel at detecting misfires, which can result from various issues such as faulty spark plugs, damaged wires, or a malfunctioning ignition coil. Detecting misfires promptly is important to prevent potential damage to the engine.
Power Inverters
Power inverters are vital tools in diagnosing electrical issues in vehicles. Voltage output testing is essential for determining if the inverter is functioning correctly. Additionally, waveform analysis techniques and load capacity evaluation are key aspects to take into account for a thorough diagnostic process.
Voltage Output Testing
Conducting voltage output testing on power inverters requires a methodical approach to guarantee accurate diagnostics. To effectively analyze the voltage output of a power inverter, follow these key steps:
- Check for Voltage Drop: Verify there are no significant voltage drops across the inverter components to identify any potential issues.
- Perform Circuit Analysis: Conduct a thorough circuit analysis to pinpoint any areas of concern or malfunction within the power inverter.
- Verify Input Voltage: Confirm that the input voltage to the inverter falls within the specified range for best performance.
- Inspect Output Connections: Inspect the output connections for any loose wires or faulty connections that may affect the voltage output.
Waveform Analysis Techniques
Analyzing waveforms in power inverters provides essential insights into the performance and functionality of the system. Signal interpretation is critical in diagnosing issues and ensuring best operation. By utilizing waveform analysis techniques, such as observing voltage patterns over time, I can pinpoint abnormalities that may indicate potential problems within the power inverter. Understanding the intricacies of waveform analysis allows me to interpret data accurately, leading to effective troubleshooting and maintenance. By mastering these techniques, I can enhance the efficiency and reliability of power inverters, ultimately benefiting the machinery they support. Waveform analysis empowers me to deliver precise diagnostics and solutions, ensuring that the power inverters operate at their best capacity.
Load Capacity Evaluation
Observing load capacity in power inverters plays a pivotal role in determining their operational efficiency and performance. When evaluating load capacity, the following points are essential:
- Weight Distribution Analysis: Understanding how weight is distributed across the inverter helps in optimizing its performance and preventing overloading.
- Load Bearing Capacity Assessment: Evaluating the maximum load that the inverter can handle guarantees it operates within safe limits.
- Efficient Power Output: Matching the load capacity with the power requirements guarantees efficient functioning without strain.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly checking load capacity helps in identifying potential issues early, preventing breakdowns and costly repairs.
Diagnostic Software
Modern diagnostic software empowers mechanics to efficiently pinpoint and resolve vehicle issues with precision. By leveraging software integration strategies and advanced diagnostic algorithms, mechanics can streamline their diagnostic processes and enhance the accuracy of their assessments. These tools allow for in-depth data analysis techniques, enabling mechanics to interpret intricate vehicle data effectively.
To illustrate the capabilities of diagnostic software, consider the following table showcasing common features and benefits:
| Feature | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Software Integration | Seamless data sharing between systems |
| Advanced Diagnostic Algorithms | Enhanced fault detection capabilities |
| Data Analysis Techniques | Thorough analysis of vehicle performance |
| System Performance Optimization | Fine-tuning vehicle systems for efficiency |
| User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive tools for easy navigation |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Instant feedback on vehicle parameters |
Through these features, diagnostic software not only aids in identifying issues but also optimizes system performance. Mechanics can make informed decisions backed by advanced algorithms and real-time data, leading to quicker and more accurate repairs. This level of sophistication in diagnostic software is invaluable for modern mechanics aiming to deliver exceptional service to their customers.
Pressure Gauges
When addressing vehicle diagnostics, the utilization of pressure gauges becomes pivotal in evaluating critical system parameters accurately. Pressure gauges are essential tools for mechanics, providing valuable insights into the inner workings of a vehicle’s systems. Here are some key points to take into account:
-
Proper Calibration: Ensuring pressure gauge calibration is up to date is essential for accurate readings. Regular calibration checks guarantee the reliability of the measurements taken during diagnostic procedures.
-
Advanced Techniques: Utilizing pressure gauges goes beyond basic pressure readings. Advanced techniques involve interpreting pressure variations over time, analyzing peak pressures, and understanding pressure fluctuations within systems.
-
Engine Performance Analysis: Pressure gauges are particularly useful for engine performance analysis. By connecting gauges to different points in the engine system, mechanics can pinpoint issues such as low compression, intake leaks, or exhaust restrictions affecting performance.
-
System Troubleshooting: Pressure gauges aid in troubleshooting various vehicle systems, including the fuel system, cooling system, and hydraulic systems. By measuring pressure levels at critical points, mechanics can identify blockages, leaks, or malfunctions impacting system performance.
Inspection Cameras
Utilizing inspection cameras revolutionizes the way mechanics conduct detailed visual assessments of hard-to-reach areas in vehicles. These tools offer a range of benefits, such as enabling me to inspect areas that are otherwise inaccessible without major disassembly, saving time and effort. The high-resolution images provided by inspection cameras allow for precise identification of issues, leading to accurate diagnoses and efficient repairs.
One drawback of inspection cameras is their limited field of view, which can sometimes make it challenging to navigate through complex systems. However, with experience and creativity, I have found various ways to overcome this limitation. For instance, by combining the camera with a flexible probe, I can maneuver through tight spaces and around corners to capture thorough visuals.
In addition to traditional diagnostic uses, inspection cameras have proven to be versatile tools in my arsenal. I frequently use them for inspecting engine components, identifying leaks, and even retrieving small parts that have fallen into inaccessible areas. Their compact size and maneuverability make them invaluable for detecting issues early on and preventing more extensive damage.