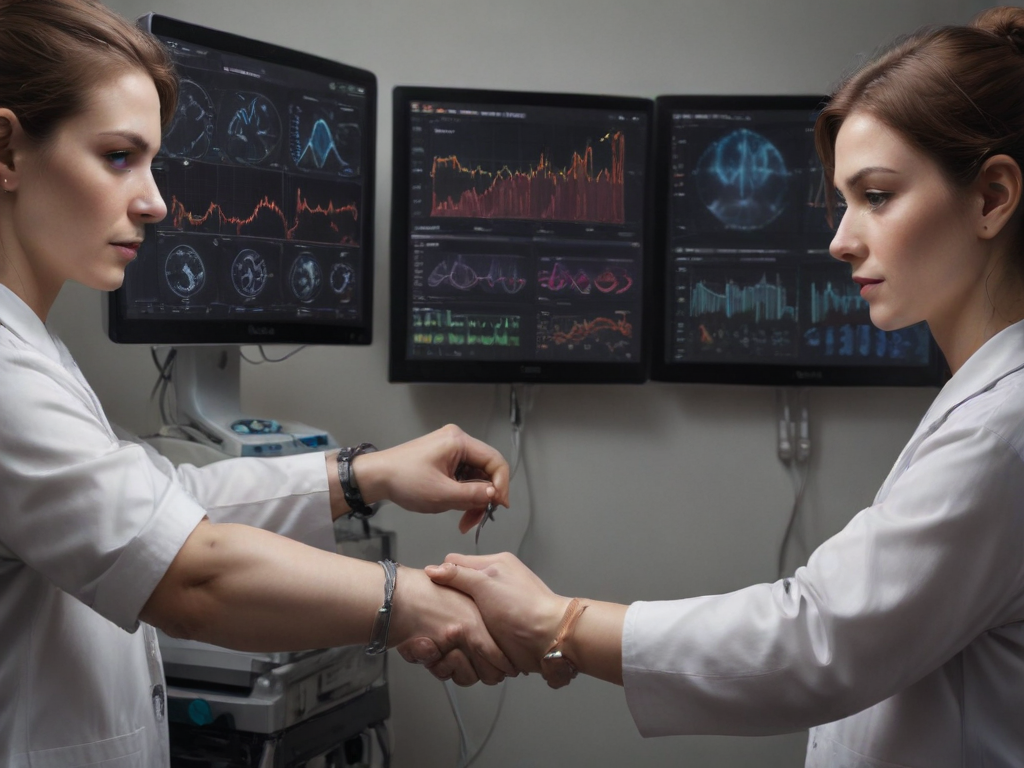
Like a navigator relying on a sophisticated compass, advanced diagnostic tools for fluid management guide healthcare professionals in understanding the intricate balance of bodily fluids. These tools go beyond basic assessments, offering insights that were once elusive.
From non-invasive imaging techniques to real-time biomarker analysis, the landscape of fluid monitoring is rapidly evolving, promising enhanced precision and proactive intervention.
As we explore the realm of these cutting-edge technologies, we uncover a horizon filled with possibilities that could revolutionize patient care in ways we have yet to fathom.
Importance of Fluid Monitoring Tools
Fluid monitoring tools are essential for accurately assessing and managing patients’ fluid status. As a healthcare professional, I rely heavily on these tools to make informed decisions about fluid therapy and patient care. By utilizing devices such as bedside ultrasound machines, I can quickly visualize a patient’s internal organs and detect any signs of fluid overload or depletion. This real-time imaging allows me to adjust treatment plans promptly and improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, tools like central venous pressure monitors provide me with valuable information about a patient’s fluid volume and cardiac function. By measuring the pressure in the vena cava, I can assess how effectively the heart is pumping blood and whether adjustments to fluid therapy are necessary. These tools are especially crucial in critically ill patients or those undergoing major surgeries where fluid balance plays a significant role in recovery.
Types of Advanced Imaging Techniques
Utilizing cutting-edge technology, various advanced imaging techniques offer healthcare professionals detailed insights into patients’ internal anatomy and pathology. These tools play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing fluid-related disorders effectively. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides high-resolution images of soft tissues and is particularly useful in assessing brain and spinal cord abnormalities. Computed Tomography (CT) scans use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, aiding in the detection of fluid accumulations or abnormalities in organs. Ultrasound imaging, which utilizes sound waves to produce real-time images, is valuable for visualizing fluid pockets in the abdomen or chest. Below is a table summarizing these advanced imaging techniques:
| Imaging Technique | Principle | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images | Brain and spinal cord abnormalities |
| Computed Tomography (CT) | Combines X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images | Detection of fluid accumulations or organ abnormalities |
| Ultrasound Imaging | Utilizes sound waves for real-time imaging | Visualizing fluid pockets in the abdomen or chest |
Role of Biomarkers in Fluid Management
I’ll kick off the discussion of biomarkers in fluid management by highlighting their crucial role in assessing hydration levels, monitoring fluid balance, and providing early detection of potential imbalances.
These biomarkers offer valuable insights into an individual’s hydration status, aiding in the timely adjustment of fluid intake or therapy.
Biomarkers for Hydration
When considering fluid management, the role of biomarkers in assessing hydration levels is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Biomarkers provide valuable insights into an individual’s hydration status by indicating specific changes in the body.
Here are four key reasons why biomarkers are essential in fluid management:
-
Precision: Biomarkers offer precise measurements that help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs.
-
Early Detection: They enable early detection of dehydration or overhydration, allowing for prompt intervention before complications arise.
-
Monitoring Progress: Biomarkers help in monitoring the effectiveness of fluid management strategies over time.
-
Personalized Care: By utilizing biomarkers, healthcare professionals can provide personalized care that optimizes hydration levels for improved patient outcomes.
Monitoring Fluid Balance
Biomarkers play a crucial role in monitoring fluid balance as they provide valuable insights into an individual’s hydration status. These biomarkers, such as urine specific gravity, blood urea nitrogen, and plasma osmolality, help healthcare professionals assess whether a person is adequately hydrated or experiencing dehydration.
Early Detection Methods
Utilizing key biomarkers facilitates early detection of fluid imbalances, guiding timely interventions for optimal fluid management. When it comes to fluid balance, biomarkers play a crucial role in identifying deviations from the norm.
Here are four ways in which biomarkers aid in the early detection of fluid imbalances:
-
Renal Biomarkers: Monitoring levels of biomarkers like NGAL can indicate acute kidney injury, a common cause of fluid retention.
-
Cardiac Biomarkers: Elevated levels of BNP can signal heart failure, prompting adjustments in fluid therapy.
-
Electrolyte Biomarkers: Tracking electrolyte levels such as sodium and potassium helps prevent imbalances that can affect fluid distribution.
-
Inflammatory Biomarkers: Monitoring markers like CRP assists in detecting inflammation-related fluid shifts early on.
Utilizing Point-of-Care Testing Devices
Point-of-care testing devices provide rapid and convenient diagnostic information for fluid management. These portable devices offer immediate results, allowing healthcare providers to make timely decisions regarding fluid interventions. By utilizing point-of-care testing devices, we can quickly assess electrolyte levels, kidney function, and other essential markers in fluid analysis.
Below is a table highlighting the key advantages of point-of-care testing devices in fluid management:
| Advantages of Point-of-Care Testing Devices |
|---|
| Rapid results |
| Portable and convenient |
| Immediate decision-making |
| Assess electrolyte levels quickly |
| Monitor kidney function efficiently |
Benefits of Continuous Monitoring Systems
Continuous monitoring systems offer a real-time approach to tracking fluid dynamics in clinical settings. These systems provide invaluable benefits that enhance patient care and streamline medical processes. Here are four advantages of utilizing continuous monitoring systems:
-
Timely Detection: Continuous monitoring allows for the immediate detection of changes in fluid levels or dynamics, enabling prompt intervention and preventing complications.
-
Accurate Trend Analysis: By continuously tracking fluid parameters, these systems provide a comprehensive view of trends over time, aiding in the early identification of potential issues.
-
Enhanced Patient Safety: Real-time monitoring ensures that healthcare providers can quickly respond to any deviations from normal fluid levels, thus enhancing patient safety and outcomes.
-
Optimized Treatment Plans: The data obtained from continuous monitoring systems helps in tailoring personalized treatment plans, leading to improved patient management and overall care quality.
Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Fluid Assessment
How can artificial intelligence revolutionize fluid assessment in clinical practice?
Artificial intelligence offers a promising solution to enhance fluid assessment by analyzing large volumes of data quickly and accurately. AI algorithms can process data from various sources, such as continuous monitoring systems and wearable sensors, to provide real-time insights into a patient’s fluid status. By integrating AI into fluid assessment, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions regarding fluid management, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced risks of complications.
AI can analyze trends and patterns in fluid levels, detect subtle changes that may indicate early signs of fluid imbalance, and even predict future fluid needs based on individual patient data. This proactive approach enables healthcare professionals to intervene promptly, preventing potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, AI can help optimize fluid therapy by personalizing treatment plans to each patient’s specific needs, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of care.
Integration of Wearable Sensors
I explore the significance of sensor data collection in fluid management, emphasizing real-time monitoring capabilities to enhance patient care.
The analytical insights derived from wearable sensors provide healthcare professionals with valuable information for informed decision-making.
This integration offers a comprehensive approach to fluid management, improving patient outcomes through proactive monitoring and timely interventions.
Sensor Data Collection
Regularly monitoring vital signs through the integration of wearable sensors provides real-time data for accurate fluid management in healthcare settings. These sensors offer valuable insights into a patient’s condition, allowing for timely interventions and personalized treatment plans.
Here are four key benefits of sensor data collection:
-
Continuous Monitoring: Wearable sensors enable round-the-clock tracking of vital signs, ensuring that any fluctuations are immediately detected.
-
Data Accuracy: The real-time data collected by sensors is precise and reliable, providing healthcare professionals with up-to-date information for making informed decisions.
-
Early Warning Systems: By analyzing sensor data, healthcare providers can set thresholds and receive alerts when a patient’s vital signs deviate from the norm.
-
Improved Patient Outcomes: The timely data provided by wearable sensors can lead to faster interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and recovery rates.
Real-time Monitoring
Integrating wearable sensors for real-time monitoring enhances healthcare professionals’ ability to track vital signs continuously, ensuring prompt detection of any fluctuations. These sensors provide valuable data points that can be crucial in managing patients’ fluid levels effectively. By leveraging wearable technology, clinicians can remotely monitor patients and intervene swiftly if any abnormalities arise. Here is a comparison table showcasing the benefits of real-time monitoring using wearable sensors:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Continuous Monitoring | Allows for round-the-clock tracking of vital signs. |
| Early Warning System | Enables rapid detection of any deviations from normal parameters. |
| Improved Patient Care | Facilitates timely interventions, leading to better patient outcomes. |
| Enhanced Data Accuracy | Provides precise and real-time data for more informed decision-making. |
Analytical Insights
Utilizing wearable sensors for analytical insights enhances the ability to extract valuable data for improved fluid management strategies. These sensors offer real-time information, allowing for prompt adjustments to fluid intake and electrolyte balance.
Here are four ways wearable sensors revolutionize fluid management:
-
Continuous Monitoring: Wearable sensors provide uninterrupted data collection, offering a comprehensive view of fluid dynamics throughout the day.
-
Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing individual hydration needs and sweat composition, tailored fluid intake recommendations can be generated.
-
Early Detection: Abnormal fluid levels or electrolyte imbalances can be detected early, enabling timely interventions to prevent complications.
-
Tracking Performance: Monitoring hydration status during physical activities helps optimize performance and prevent dehydration-related issues.
Future Trends in Fluid Management Technology
Looking ahead, advancements in fluid management technology are poised to revolutionize the way healthcare professionals monitor and regulate patients’ fluid levels. One exciting trend is the development of implantable sensors that can continuously measure various fluid parameters in real-time, providing clinicians with immediate data for prompt interventions. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence algorithms into fluid management systems will enhance the predictive capabilities, enabling early detection of fluid imbalances and personalized treatment plans. Furthermore, the miniaturization of devices allows for non-invasive monitoring, increasing patient comfort and compliance with fluid management protocols.
| Future Trends in Fluid Management Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Implantable Sensors | Real-time monitoring |
| Artificial Intelligence Integration | Predictive capabilities |
| Miniaturization of Devices | Non-invasive monitoring |
These advancements hold great promise for optimizing patient outcomes by ensuring precise fluid balance adjustments tailored to individual needs. By embracing these future technologies, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care and improve patient safety in fluid management practices.
Conclusion
As I reflect on the incredible advancements in fluid management tools, I can’t help but see them as a symphony of harmony and precision. Like a skilled conductor leading an orchestra, these technologies work together seamlessly to ensure the perfect balance and rhythm of fluid levels in the body.
With such innovative tools at our disposal, we can orchestrate optimal health and well-being for all.